HEEL SPURS
Assessment and management of heel bone overgrowth
Assessment and management of heel bone overgrowth
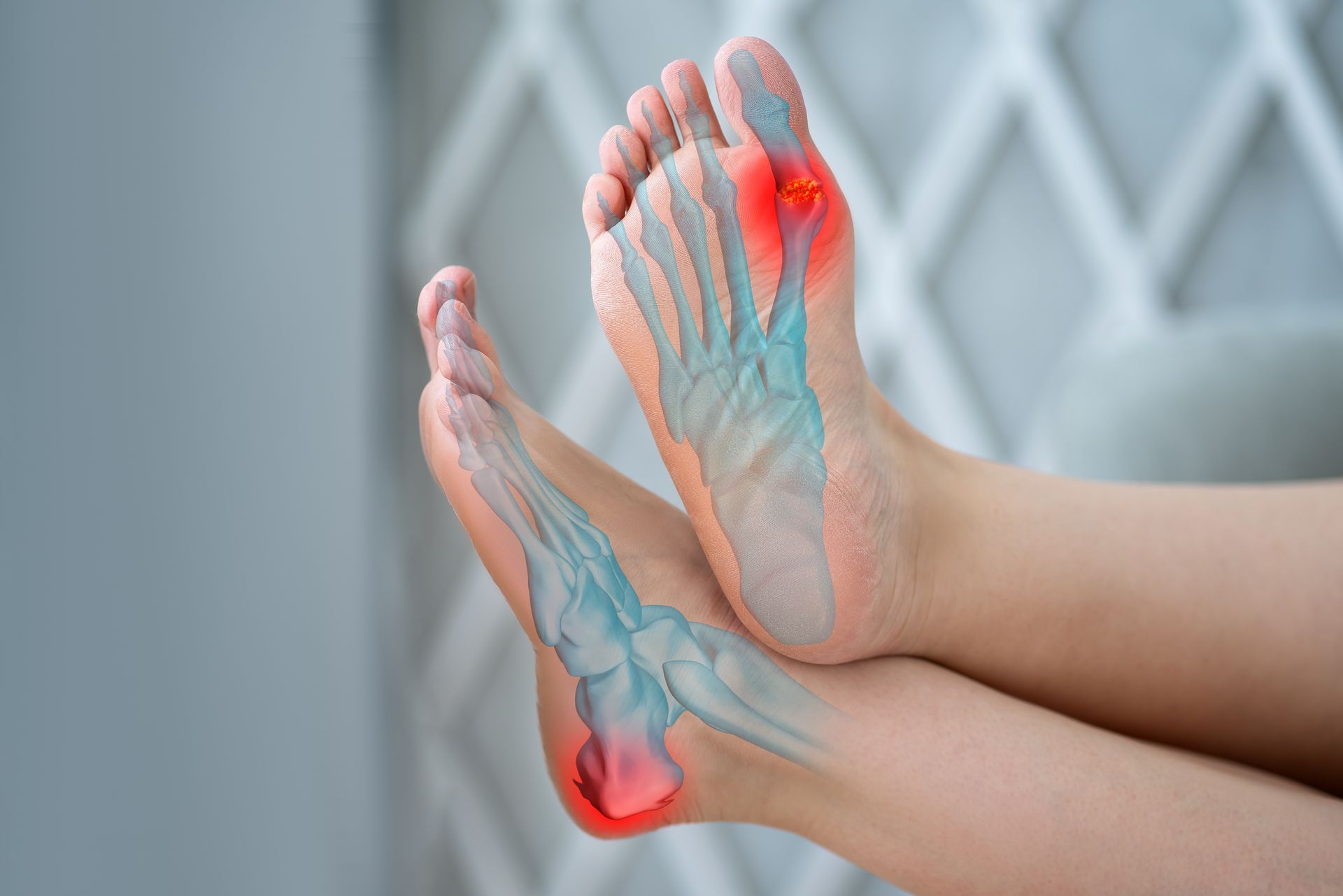
BONE CHANGES AT THE HEEL
AN OVERVIEW OF HEEL SPURS
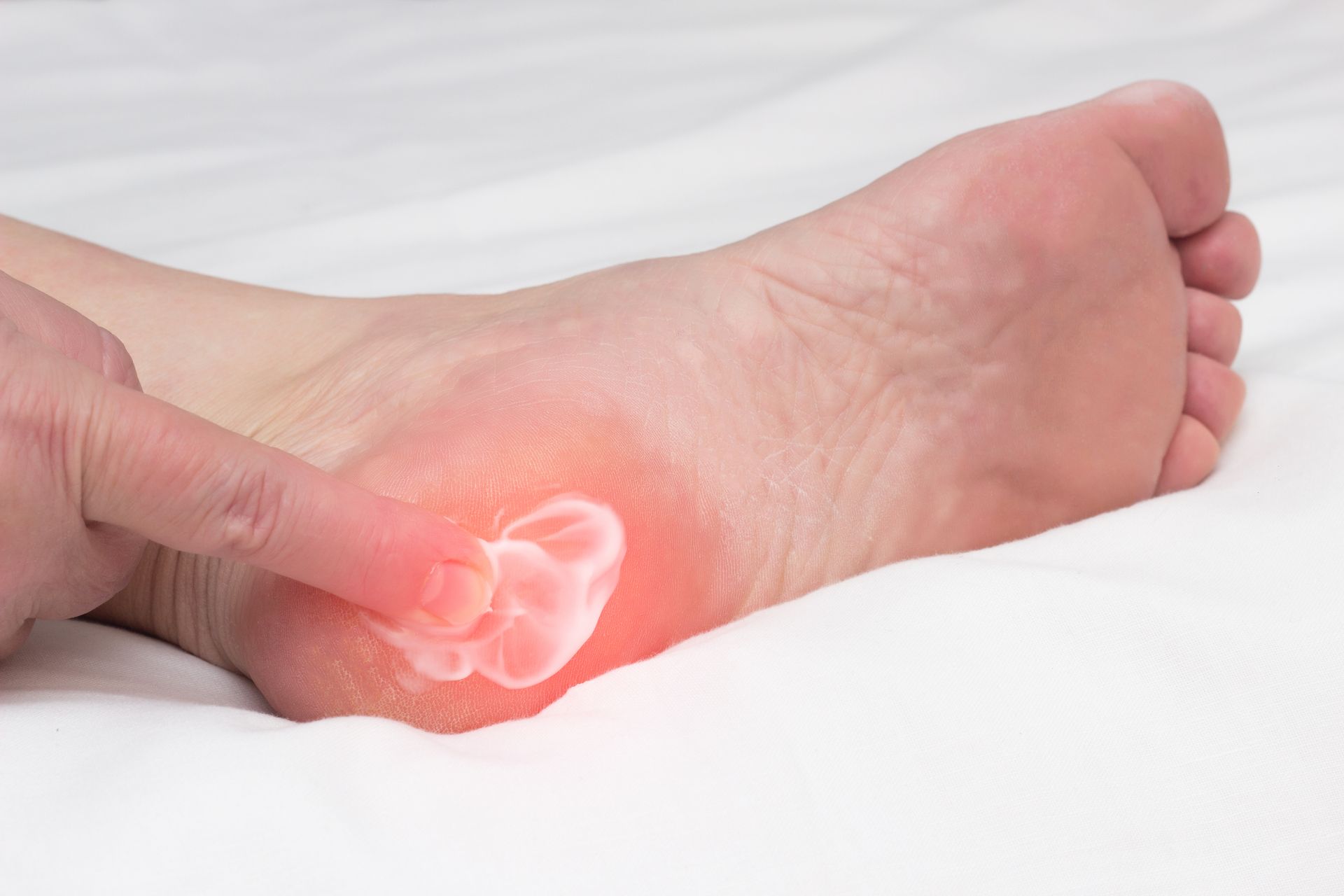
Heel spurs are formed when mineral deposits accumulate on the heel bone over an extended period. This process is often associated with ongoing mechanical stress placed on the heel and the structures that attach to it.
While some individuals are unaware of their presence, others experience discomfort related to surrounding tissue irritation. Identifying when a heel spur is contributing to symptoms is an important step in determining appropriate care.
BONE CHANGES AT THE HEEL
AN OVERVIEW OF HEEL SPURS
Heel spurs are formed when mineral deposits accumulate on the heel bone over an extended period. This process is often associated with ongoing mechanical stress placed on the heel and the structures that attach to it.
While some individuals are unaware of their presence, others experience discomfort related to surrounding tissue irritation. Identifying when a heel spur is contributing to symptoms is an important step in determining appropriate care.
BONE CHANGES AT THE HEEL
AN OVERVIEW OF HEEL SPURS
Heel spurs are formed when mineral deposits accumulate on the heel bone over an extended period. This process is often associated with ongoing mechanical stress placed on the heel and the structures that attach to it.
While some individuals are unaware of their presence, others experience discomfort related to surrounding tissue irritation. Identifying when a heel spur is contributing to symptoms is an important step in determining appropriate care.
WHEN IRRITATION BEGINS AT THE HEEL
Bone overgrowth does not always cause discomfort, but irritation may develop within nearby soft tissue. When this occurs, symptoms can gradually appear during daily movement or prolonged activity.
Symptoms that may prompt evaluation include:
- Sensitivity along the heel during weight-bearing
- Discomfort after periods of inactivity
- Local soreness that increases with standing or walking
- Changes in comfort during routine activities
- Local soreness that increases with standing or walking
- Changes in comfort during routine activities
- Sensitivity along the heel during weight-bearing
- Discomfort after periods of inactivity
- Local soreness that increases with standing or walking
- Changes in comfort during routine activities
Clinical evaluation helps clarify whether these symptoms are related to a heel spur or another source of heel irritation.
HOW HEEL SPURS CAN AFFECT MOVEMENT
When irritation occurs around a heel spur, it may influence walking patterns, posture, and overall comfort. Over time, individuals may adjust how they bear weight to avoid discomfort, which can place added stress on other areas of the foot or lower extremity.
Addressing contributing factors early helps reduce ongoing strain and supports more balanced movement during daily activity.
When irritation occurs around a heel spur, it may influence walking patterns, posture, and overall comfort. Over time, individuals may adjust how they bear weight to avoid discomfort, which can place added stress on other areas of the foot or lower extremity.
Addressing contributing factors early helps reduce ongoing strain and supports more balanced movement during daily activity.
BASED ON STRUCTURAL FINDINGS
APPROACHES FOR HEEL SPUR MANAGEMENT
Recommendations are guided by symptom presentation, imaging findings, and how surrounding tissue is affected. Care is focused on easing irritation, supporting adjacent structures, and improving functional movement rather than addressing bone changes alone.
Planning also considers activity demands, footwear choices, and biomechanical stressors that may contribute to ongoing strain. This allows guidance to be aligned with both clinical findings and daily movement needs.
The following approaches are considered:
Conservative Care:
- Evaluation of heel structure and surrounding tissue
- Supportive footwear or orthotic recommendations
- Stretching or activity modification strategies
- Measures to reduce localized stress and irritation
- Monitoring response over time
Surgical Solutions:
- Surgical intervention considered only when symptoms persist
- Procedures selected based on structural findings and response to care
- Focus on relieving irritation and restoring functional comfort
Surgical options are considered selectively and only when other measures do not provide adequate improvement.
BASED ON STRUCTURAL FINDINGS
APPROACHES FOR HEEL SPUR MANAGEMENT
Recommendations are guided by symptom presentation, imaging findings, and how surrounding tissue is affected. Care is focused on easing irritation, supporting adjacent structures, and improving functional movement rather than addressing bone changes alone.
Planning also considers activity demands, footwear choices, and biomechanical stressors that may contribute to ongoing strain. This allows guidance to be aligned with both clinical findings and daily movement needs.
The following approaches are considered:
Conservative Care:
- Evaluation of heel structure and surrounding tissue
- Supportive footwear or orthotic recommendations
- Stretching or activity modification strategies
- Measures to reduce localized stress and irritation
- Monitoring response over time
Surgical Solutions:
- Surgical intervention considered only when symptoms persist
- Procedures selected based on structural findings and response to care
- Focus on relieving irritation and restoring functional comfort
Surgical options are considered selectively and only when other measures do not provide adequate improvement.
BASED ON STRUCTURAL FINDINGS
APPROACHES FOR HEEL SPUR MANAGEMENT
Recommendations are guided by symptom presentation, imaging findings, and how surrounding tissue is affected. Care is focused on easing irritation, supporting adjacent structures, and improving functional movement rather than addressing bone changes alone.
Planning also considers activity demands, footwear choices, and biomechanical stressors that may contribute to ongoing strain. This allows guidance to be aligned with both clinical findings and daily movement needs.
The following approaches are considered:
Conservative Care:
- Evaluation of heel structure and surrounding tissue
- Supportive footwear or orthotic recommendations
- Stretching or activity modification strategies
- Measures to reduce localized stress and irritation
- Monitoring response over time
Surgical Solutions:
- Surgical intervention considered only when symptoms persist
- Procedures selected based on structural findings and response to care
- Focus on relieving irritation and restoring functional comfort
Surgical options are considered selectively and only when other measures do not provide adequate improvement.